
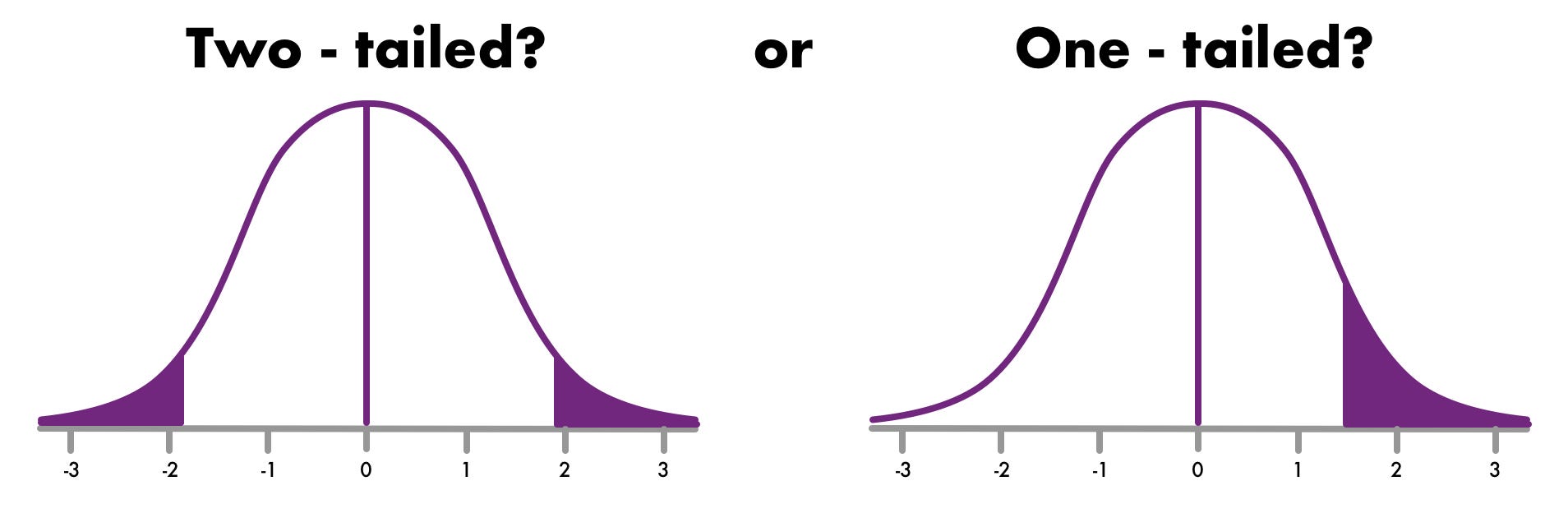
Step 2: Specify the Alternative Hypothesis


There is no difference in intubation rates across ages 0 to 5 years.In research studies, a researcher is usually interested in disproving the null hypothesis. The null hypothesis (H 0) is a statement of no effect, relationship, or difference between two or more groups or factors. Calculate the Test Statistic and Corresponding P-Value.This is formally done through a process called hypothesis testing. Based on this information, you'd like to make an assessment of whether any differences you see are meaningful, or if they are likely just due to chance. When you are evaluating a hypothesis, you need to account for both the variability in your sample and how large your sample is. To evaluate whether these protocols were successful in improving intubation rates, you could measure the intubation rate over time in one group randomly assigned to training in the new protocols, and compare this to the intubation rate over time in another control group that did not receive training in the new protocols. Hypothesis testing is generally used when you are comparing two or more groups.įor example, you might implement protocols for performing intubation on pediatric patients in the pre-hospital setting.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
